June 28 2024 | By Farwah Jafri | 8 minutes Read

W2 vs W4 form Comparison
What is a W4 Form?
Key Information on a W4 Form
What is a W2 Form?
Key Information on a W2 Form
W2 vs W4 Form: Key Differences
W2 vs W4 Form: Why They Matter
For Employees
For Employers
How to Complete a W2 Form
Sections A to F
How to Complete a W4 Form
Common Questions
1. Do I Need to Fill Out a W4 Every Year?
2. What Happens If I Don’t Fill Out a W4 Correctly?
3. Can I Update My W4 Form Mid-Year?
4. What Should I Do If I Lose My W2 Form?
Final Thoughts
Understanding the varying types of tax forms can leave even expert accountants scratching their heads. Two of the documents that confuse many businesspeople are the W2 and W4 forms. Let’s break down the W2 vs W4 form comparison, making it easier for you to understand the forms’ purposes, differences, and significance.
Here’s all the basic information you need to know!
The IRS W4 form, also known as the Employee’s Withholding Certificate, is a document an employee would typically fill out upon hiring (or if their withholding or filing status changes). This is primarily done to inform the employer of the specific amount of tax to withhold from the employee’s paycheck.
This form typically requires an employee to inform you about their tax filing status; whether they are single, head of household, married filing jointly, or married filing separately. It also tells you all you need to know about whether they work additional jobs, have a spouse who is employed, or claim dependents. In certain states, a specific state version of the W-4 form is also required so state income taxes can also be withheld from their salary.
The W4 form includes the following sections:
The IRS W2 Form, also known as an employee’s Wage and Tax Statement, is filled out by an employer for each employee who is paid $600 at the very least for the tax year. This also needs to be filed with the Social Security Administration (SSA).
The W2 Form is primarily used to record how much your employees are paid, including their wages, tips, if any, and other kinds of benefits they receive as well as Medicare, Social Security, state-based taxes, and much more.
Employers need to keep in mind that they are required by law to fill out, file, and distribute a W2 form for each employee who is paid at least $600 within the given tax year, even if they are no longer employed. These forms can be distributed and filed electronically. In fact, payroll services such as Gusto make it much easier to manage this.
The W2 form contains multiple sections, each providing specific information:
What is the W2 and W4 difference that stands out for you? Here are some key differences you can keep in mind
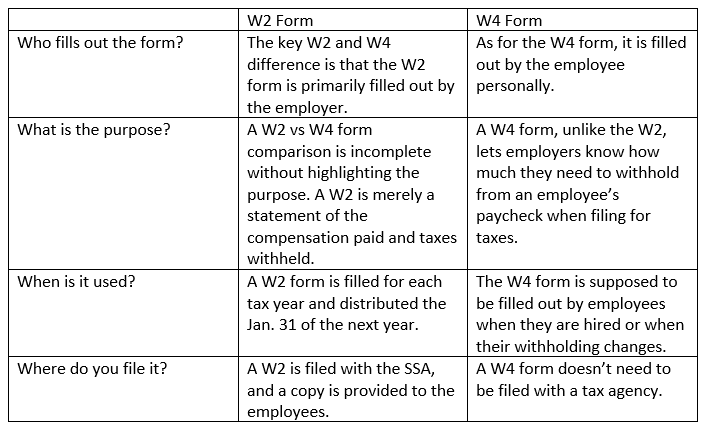
Understanding the w2 vs w4 form is essential for effective tax management. Here’s why they matter:
You can complete your W2 form either manually or by using payroll software. The W2 form is divided into boxes labeled from A to F and 1 to 20. Follow these steps to complete it accurately:
Fill out these sections with the employee’s and employer’s details. This includes the employee’s name, address, Social Security number, and the employer’s name, address, and Employer Identification Number (EIN). If your business does not use control numbers, you can leave the relevant boxes blank.
New employees usually fill out the W4 form during the onboarding process. Follow these steps to complete it:
Following these steps will ensure your W2 and W4 forms are filled out correctly, aiding in accurate tax reporting and withholding.
No, you only need to fill out a new W4 form when you start a new job or want to adjust your tax withholdings. The W2 form, however, is issued annually by your employer.
Incorrectly filling out a W4 form can result in too much or too little tax being withheld from your paycheck. This can lead to a large tax bill or a smaller refund when you file your taxes. It’s important to use the IRS’s online estimator or consult with a tax professional to fill out the W4 form accurately.
Yes, you can update your W4 form at any time during the year if you experience changes in your financial situation, such as getting married, having a child, or getting a second job. Updating your W4 ensures that the correct amount of tax is withheld from your paycheck.
If you lose your W2 form, contact your employer to request a new copy. Employers are required to keep copies of W2 forms for several years and can provide you with a replacement. You can also contact the IRS for assistance if you cannot obtain a copy from your employer.

Understanding the differences between the w2 vs w4 form doesn’t have to be overwhelming. By understanding their purposes and how to properly use them, you can manage your taxes more effectively.
The W2 form provides a summary of your earnings and taxes withheld over the year, essential for filing your annual tax return. The W4 form allows you to control the amount of tax withheld from your paycheck, ensuring you pay the correct amount of tax throughout the year.
By staying informed and accurately managing these forms, both employees and employers can ensure compliance with tax regulations and avoid potential issues with the IRS. Whether you’re starting a new job, adjusting your withholdings, or preparing to file your taxes, understanding the differences between the w2 vs w4 form is a crucial step in effective tax management.
Looking to make your tax season easier? Perhaps a financial expert is just what you need! Monily’s experts can dedicate their attention to your tax concerns and add efficiency to the process so you can focus on your core functions! Contact our experts today and learn more.
Subscribe for business tips, tax updates, financial fundamentals and more.
MORE BLOGS

Running a startup or a small business is all about making smart decisions, especially when it comes to spending money. Every dollar counts and before investing […]
Learn More →
It can be quite hard to trust software to do all your accounting for you right off the bat. All new additions to your workflow take […]
Learn More →
We already detailed in a previous blog here, what NetSuite is all about. In short, it is a cloud-based suite of management tools that, on a […]
Learn More →